R&D Update: New evaluation tool for degradation and sources of groundwater pollutants
Posted on Wednesday 26 May 2021 Why starting an expensive remediation project when there is sufficient Natural Attenuation?...
2 min read
 Goedele Verreydt
:
Apr 30, 2024 12:37:35 PM
Goedele Verreydt
:
Apr 30, 2024 12:37:35 PM

Posted on Tuesday 16 May 2023
Whenever sustainable degradation of pollutants in groundwater can be demonstrated, inexpensive and environmentally friendly remediation options are possible. That is why IsoFLUX was launched as new evaluation tool for degradation and sources of groundwater pollutants.
Groundwater is a vital resource that sustains human societies and ecosystems alike. However, it is susceptible to contamination from various sources, including industrial activities, agriculture, and improper waste management. To understand the behavior and fate of groundwater pollutants, isotope analysis is employed. This can be a powerful tool that unravels invaluable insights into the natural degradation processes occurring within aquifers. This article explores the significance of isotope analysis in studying groundwater pollutants and how it contributes to our understanding of natural degradation potential.
Understanding Isotope Analysis
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses due to varying numbers of neutrons. Some isotopes are stable, while others are radioactive, undergoing decay over time. Isotope analysis involves measuring the abundance of specific isotopes within a sample and comparing them to known standards or references. In the context of groundwater pollution, isotopes provide unique signatures that shed light on the origin, transport, and transformation of contaminants.
How is this relevant for quantifying natural degradation?
Isotope analysis aids in tracing the transport and fate of groundwater pollutants. Isotopic ratios change as contaminants undergo various physical, chemical, and biological processes during their migration through the subsurface. Monitoring isotopic shifts along groundwater flow paths provides valuable insights into attenuation mechanisms, such as dilution, adsorption, biodegradation, and volatilization. This information enables you to assess the effectiveness of natural attenuation processes in reducing contaminant concentrations.
Isotope analysis of groundwater pollutants offers numerous benefits for remediation strategies and sustainable water management. By understanding the natural degradation processes, decision-makers can optimize remediation efforts and minimize reliance on costly engineering interventions. Isotope analysis provides essential information for evaluating the potential for monitored natural attenuation (MNA) or enhanced bioremediation, which can harness natural processes to mitigate contamination.
Furthermore, the use of stable isotopes as tracers can aid in identifying preferential flow paths, understanding groundwater recharge mechanisms, and delineating vulnerable zones within aquifers. This knowledge can guide the implementation of targeted monitoring programs and facilitate proactive measures for preventing contamination.
How can you measure this?
Together with Isodetect and Cornet & Renard, a new measuring tool is developed. IsoFLUX is launched for time-integrated and very sensitive isotope analysis of groundwater pollutants in order to achieve:
IsoFLUX summarizedIsoFLUX provides information that can not be obtained via conventional groundwater measurements and analyses. This technology opens a more comprehensive insith into the actual migration and degradation of pollutants in groundwater.
|
What are the advantages of IsoFLUX?
The IsoFLUX provides information that can not be obtained via conventional groundwater measurements and analyses. The technology opens a more comprehensive insight into the actual migration and degradation of pollutants in groundwater, our most important natural resource for drinking water.
IsoFLUX delivers very sensitive and precise flux estimations and CSIA of groundwater pollutants like monoaromatics (BTEX), chlorinated solvents (CVOCs) as well as pesticides (e.g. phenoxy acids, desphenylchloridazone).
Batch and dynamic laboratory tests revealed precise and accurate isotope analysis reaching significantly lower levels of detection in comparison to conventional sampling procedures.
At representative field sites, contaminated with BTEX, CVOC and pesticides (2,4-dichloroprop), alpha testing of IsoFLUX samplers were successfully carried out.
Interpretation schemes using the obtained flux and CSIA data complements the IsoFLUX approach enabling meaningful and sound source contribution assessment and degradation quantification.
‘This project has received funding from the Eurostars-2 joint programme with co-funding from the European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme.’


Posted on Wednesday 26 May 2021 Why starting an expensive remediation project when there is sufficient Natural Attenuation?...
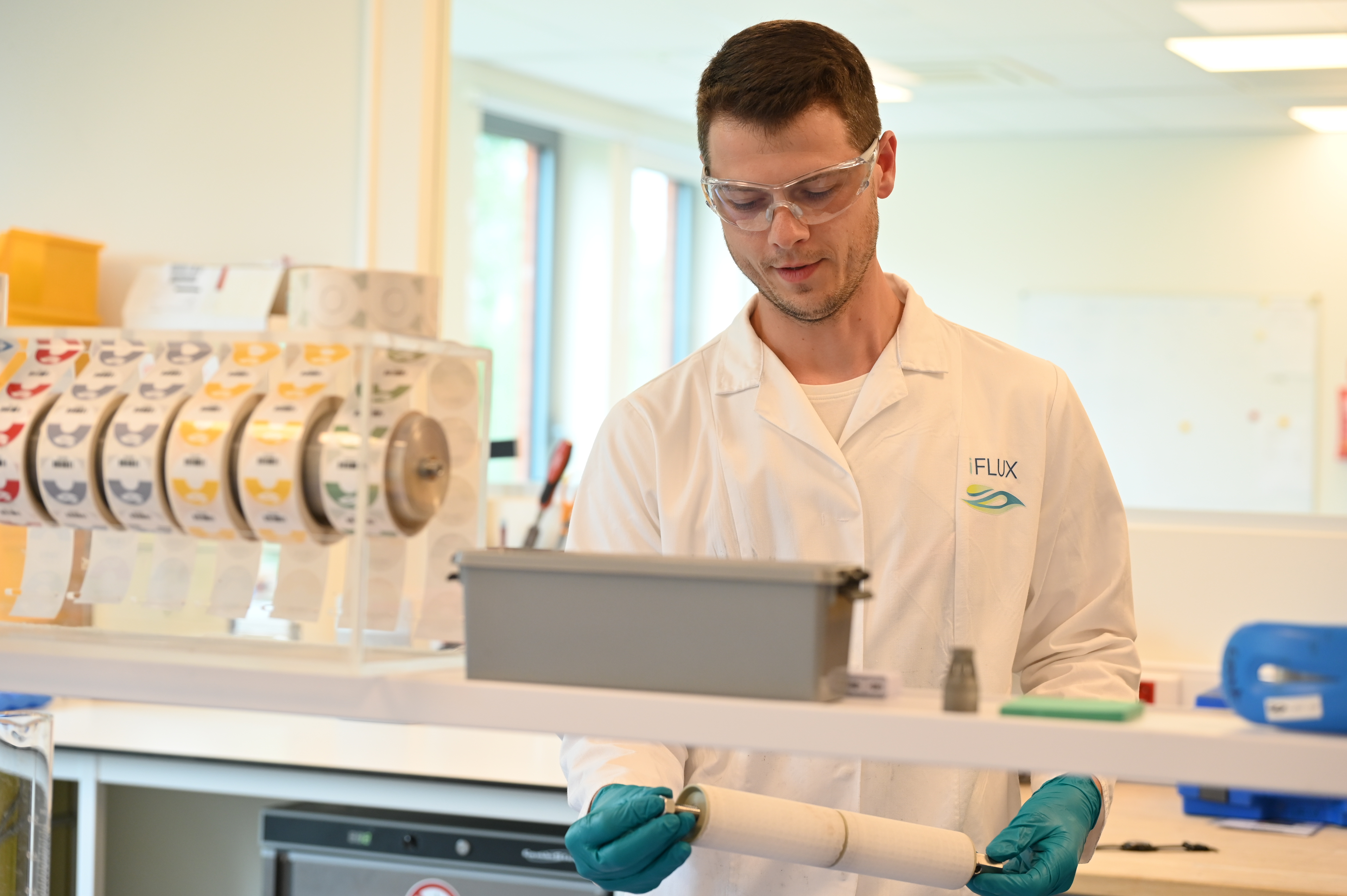

Remediation is extremely costly, so it’s best to do it in a targeted way and get it right the first time. The iFLUX Sampler is a unique tool that...
Posted on Monday 14 February 2022 iFLUX is shifting its activities from more reactive monitoring to a digital system...